This site summarizes the vendor specific model (VSM) characterization, generic model parameterization and validation for the major wind turbines in North America. The purpose of this site is to provide a comprehensive overview of the VSM behavior and the ability of the current generic models to mimic this behavior under uniform conditions in both PSLF and PSSE simulation platforms.
Test System
Main article: Test System: Simulation Model
 for characterization and parameterization simulations was designed by Yuriy Kazachkov – Siemens Energy)
for characterization and parameterization simulations was designed by Yuriy Kazachkov – Siemens Energy)
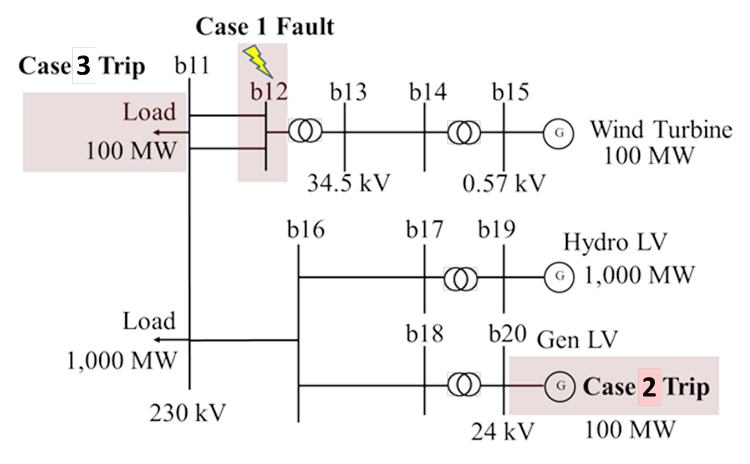
The test system, shown in figure on the right, includes an equivalent 100 MW wind power plant (WPP) and its associated unit transformer, collector system, and substation transformer. The equivalent of the collector system is represented by the branch between buses 13 and 14, with the main station transformer for the wind farm between buses 12 and 13. The High Voltage Point of Interconnection (POI) is the 230 kV bus 12. The POI is connected to the load bus 11 by a double circuit line.
Two other generators are also modeled: a 1,000 MVA hydro unit and 100 MVA gas turbine unit. Two loads of 100 MVA and 1,000 MVA are modeled as constant power loads connected to bus 11.
Test Cases
The following three test cases are documented:
- Case 1: Six-cycle (0.1 sec.), three phase fault at bus 12. The fault is cleared by tripping one of the two lines between bus 11 and bus 12.
- Case 2: Trip of a 100 MW generator at bus 20.
- Case 3: Trip of a 100 MW load at bus 11.
For all cases it is assumed that the WPP is generating rated power (100 MW).
The impedance of the double circuit line between buses 11 and 12 was adjusted to ascertain the dynamic performance of the WPP for short circuit ratios (SCRs) of 5 and 10 at the POI.
Parameterization
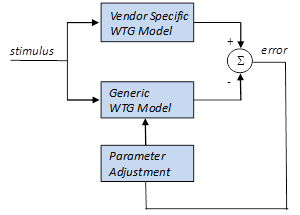
In order for the response of a dynamic model to approximate the response of a given vendor specific model (VSM), the parameters of the generic model typically need to be adjusted. This process is termed parameterization process, i.e., the parameterization process refers to the adjustment of the parameter values of a generic WTG model to best reflect the dynamic characteristics of a VSM. Conceptually, this process is depicted in Figure on the right. The figure shows a generic WTG and a VSM models subject to the same stimulus, e.g., fault, line trip, etc. The parameterization process aims at reducing the difference (error) between the dynamic responses of both models. Reducing the error may entail an algorithmic approach and/or the manual adjustment of parameters. It is recognized that, in general, the responses of the generic and VSM will not be identical. The fundamental issue to be addressed is whether a generic model properly parameterized is a suitable model for application in bulk power system studies of the type often executed in routine planning studies.
The major challenge for the parameterization of generic models comes from the fact that each VSM is designed according to the turbine vendor’s specification. This implies that the internal mechanism and control settings can be quite different even for the same type of wind turbine. Furthermore, for confidentiality reasons, critical components and parameters for many VSMs are hard-coded in the models and are not disclosed to users. Often, a VSM is regarded as “blackbox” with essentially unknown characteristics.
The objective of the parameterization part in this report is to facilitate the use of generic models by providing the generic model parameters needed for representing VSMs. This part also includes sample time domain simulations that compare the response of VSMs versus the corresponding generic models in PSLF and PSSE platforms.
